The Passivhaus concept: How to turn your home into an energy-efficient household
Reducing Entropy #12: Living comfortably, with low electricity bills and generating no greenhouse gases. Yup, it is totally possible.
In recent years, certain situations have taken place that has greatly affected the global population and its way of life. With no exceptions.
First came COVID-19, which caused the closing of our borders and imprisoned us in our homes. This pandemic brought with it rising costs for many products, as well as rising energy bills and an increase in uncertainty for each of us.
Fortunately, three years later this episode has been " surpassed". Note the emphasis on quotation marks.
Everything seemed to be calm, peace, and glory until the war between Russia and Ukraine came.
We saw and continue to see horrendous images typical of war conflicts.
What timing for war (it is NEVER good timing for one).
Just when we were recovering from the flurry of blows from the pandemic comes another left hook right on the chin of the world economy (and the world's emotional stability).
With wars always come hard blows to the world economy and this time has been no exception. Russia and Ukraine are two countries with great relevance in the food and energy sector of Europe and the world.
Russia is the main exporter of gas to the European Union and other parts of the world.
According to the International Energy Agency, Russia supplies 45% of Europe's gas.
40% of the gas is used to heat homes and 15% to generate electricity. The remaining 20% is for industrial purposes.
Russia is aware of the countries' dependence on gas, and due to conflicts of interest has decreased and even shut off gas supplies.
In the constant battle of demand and supply, the short supply of gas, and the importance of gas for European countries, prices have skyrocketed to record highs. In the last 3 months alone there has been an increase of up to 70%.
Added to the price of gas, came the second left hook to the chin: weather conditions.
Last year's winter was the longest and most severe in a long time in Europe, evidently caused by our best and worst friend: THAT’S RIGHT, you guessed it, CLIMATE CHANGE.
All this has brought to light two problems ignored in Europe:
Dependence on fossil fuels. It is important to remember that dependence is almost never a good thing (tell that to Barcelona and its Messidependence some years ago).
Most homes in Europe and the world are poorly designed in terms of energy efficiency.

Yes, most of our homes are poorly designed in terms of energy.
We suffer from long periods of heat during the summer and long periods of cold during the winter, abusing air conditioning equipment such as air conditioners, fans, and heaters.
This obviously affects the electricity bill at the end of the month. In turn, these consumptions have an impact on global warming with the generation of greenhouse gases.
In 2019 alone, households were responsible for 39% of global carbon dioxide emissions.
One way to reduce these emissions is to improve the design of homes with a focus on energy efficiency.
What if I told you that there is a standard for homes that verge on perfection in terms of energy management?
Yes, these are the so-called passive houses, better known as Passivhaus.
Passivhaus: The standard in energy-ideal homes
The Passivhaus is a home standard designed in 1988 in Darmstadt, Germany.
They are characterized mainly by consuming 70%-90% less than conventional homes, which results in a significant decrease in carbon emissions. Doing all this without sacrificing the comfort of the home.
Passivhaus or Passive Houses are recognized as the standard for the highest energy efficiency, maximum comfort, and good indoor air quality in homes or buildings.
When designing passive homes a series of studies are made taking into account the atmospheric conditions and taking advantage of the heat generated by the inhabitants and the equipment to condition these buildings.
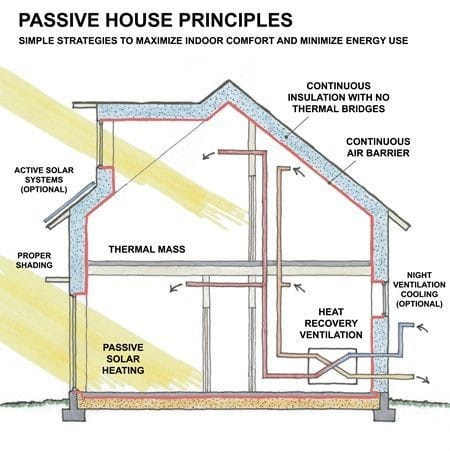
How exactly does a Passivhaus work?
The Passivhaus design depends on 5 key factors:
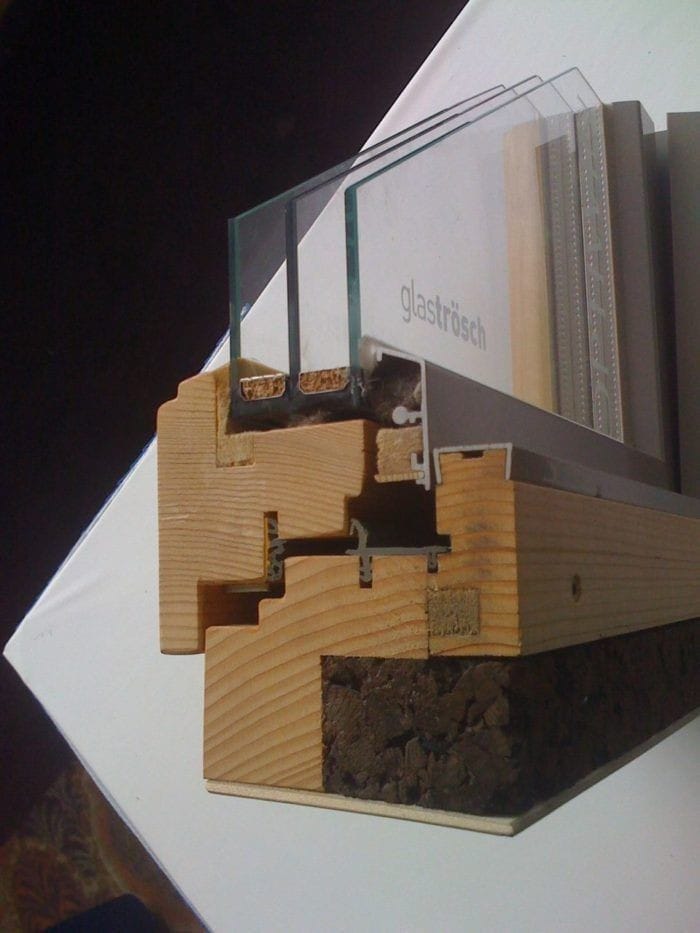
Thermal insulation: this consists of investing in components and materials that prevent heat loss from homes. These materials are placed between the walls, floor, and roof of buildings or homes.
Absence of thermal bridges: It must be verified and confirmed the non-existence of the so-called thermal bridges, which are the areas where the probability of energy losses increases. In addition to heat loss, humidity zones can be generated, which decreases the comfort and health of the inhabitants of the home.
High-quality building materials: Passivhaus buildings use windows and doors that promote thermal insulation. The windows used are characterized by having several panels and are filled with an inert gas, which guarantees not only thermal insulation but also acoustic insulation. This favors thermal insulation and energy efficiency.
Zero infiltration: There are two ways in which heat escapes or enters homes: Convection (movement of flows, such as air and water) and Conduction (heat transfer between two surfaces). The major culprit of energy loss is convection. To avoid this, the facades and floors of the Passivhaus are covered to ensure their air tightness.
Conditioning of the home: The Passivhaus replace conventional air conditioning equipment, such as air conditioning and heating, with mechanical ventilation with heat recovery (VMC). This equipment is responsible for renewing the air, and reducing and preventing diseases and infections in the respiratory tract. They are an essential part to ensure the comfort and quality of air, vital to ensure the health of the inhabitants, taking in favor the heat generated by humans and the equipment present in the building.
In addition to these basic principles, other factors that are taken into account because of their importance are:
External solar protection
Natural night ventilation
Efficient lighting systems
Although they originated in Germany, a European country characterized by harsh winters, this certification can be used regardless of climatic conditions.
Proof of this is that these designs are used in 4 continents and around 40 countries.
Benefits of the Passivhaus
Using the 5 basic Passivhaus factors ensures maximum energy efficiency, air quality, and thermal comfort.
Among other benefits of a Passivhaus-certified home are:
Energy savings and minimum consumption (up to 90%)
Reduction of carbon emissions, favorable to the reduction of climate change
Maximum comfort for the inhabitants (thermal and acoustic comfort)
Revaluation of the property
Building and materials of long durability
How to convert your home into a Passivhaus
It is important to emphasize that a Passivhaus-certified home requires an investment of time and the highest quality materials. Therefore, it has a certain degree of difficulty.
However, if what is sought is to reduce heat loss and increase energy efficiency, there are some measures or actions that can be implemented:
Replace doors with more energy-efficient ones
Replace common windows with double or triple-layer windows
Installing renewable energy generation systems, such as solar panels or wind turbines
Installing insulation in the roof and walls of the house (this is done by insulating the inside of the walls)
Installing new ventilation systems that incorporate heat recovery
Checking current heat systems and confirming that there are no leaks
The transformation of a household towards a Passivhaus certification requires investment and work, however, it is rewarded in a relatively short time with the reduction of the electricity bill, and it is environmentally friendly.
Despite being a concept that emerged at the end of the last century, the Passivhaus has been modernized in recent years as a solution to the problems that end up affecting people, both economically and socially.
They are a suitable alternative not only for families who cannot afford high gas prices. At the same time, they represent an important solution for the reduction of carbon dioxide emissions, which are emitted daily from homes, helping to reduce greenhouse gases and global warming.
.
.
.
Jr Nicolas of Reduce Entropy🌍
Top news of the week
Los Angeles bans oil and gas drilling within city limits - Read the full article
HSBC to stop funding new oil and gas fields as part of policy overhaul - Read the full article
Cop15: historic deal struck to halt biodiversity loss by 2030 - Read the full article
Other publications you might be interested in
How to do laundry in a sustainable way - Read the full article
I was totally wrong about Environmental Activism - Read the full article
Reducing the Electric Bill: Saving the World while Saving Money - Read the full article